Buyer persona surveys help businesses better understand their customers, improve brand loyalty, and create more effective marketing strategies. A buyer persona is a semi-fictional profile built using demographic and psychographic data that represents a company’s ideal customer. Surveys are a scalable and efficient way to gather this data, capturing customer goals, pain points, motivations, and behaviors. By combining survey insights with existing customer data, companies can develop multiple personas for different audience segments, both B2C and B2B. Well-designed buyer persona surveys lead to more targeted marketing, improved customer experiences, stronger lead quality, and more efficient advertising spend.
How well do you know your customers? Today, understanding customers is becoming increasingly important to encourage brand loyalty. In fact, studies show that 66% of customers expect companies to understand their needs, and that customer-centric companies are 60% more profitable than those that don’t focus on customers. One way savvy companies, and the market researchers working for them, get to know their customers is by creating buyer personas.
In this blog, we’ll discuss buyer personas with examples and show how surveys can help inform them. This article serves as a beginner’s guide to using surveys for creating effective buyer personas.
What is a Buyer Persona and Why is it Important?
A buyer persona, sometimes referred to as a user or customer persona, is a semi-fictional representation of the various potential buyers of a product or service. Developed in the 1990s by Alan Cooper, known as the founding father of personas, he championed their use to create more user-friendly products. “Personas provide us with a precise way of thinking and communicating about how users behave, how they think, what they wish to accomplish, and why,” Cooper is quoted as saying.
Today, researchers use buyer personas to understand their target audiences better and build marketing campaigns that will appeal to the audience. Mapping buyer personas to each stage of the buyer’s journey helps tailor marketing efforts, ensuring messaging and content are relevant to where the customer is in their decision-making process. Understanding customer personas can also influence the buying decision by addressing specific needs, motivations, and pain points, ultimately guiding potential buyers toward choosing your product or service. After all, if a marketer fails to understand their audience, they likely will not be able to give them what they want or market to them appropriately. In addition, incorrectly marketing a product to potential buyers or using the wrong messaging can make a brand seem out of touch with its target audience, resulting in lost customers and a lot of wasted time and money.
Creating Buyer Personas
Personas are created by marketers and researchers through existing consumer data, interviews and surveys, and some educated guesses. To create a buyer persona, it is best practice to use a buyer persona template and conduct thorough market research to ensure the persona is accurate and actionable. Most buyer persona templates use demographic and psychographic details. Demographic data includes data like age, race, gender, education, income level, occupation, and so on. Psychographic data delves into how a person feels, their goals and values, challenges they face, and so on. In our blog on psychographic data, we highlighted how researchers can use both types of data to come up with an ideal buyer persona.
It’s important to understand that it’s not uncommon for a company to have a number of buyer personas. Creating multiple buyer personas for different segments allows businesses to personalize their marketing strategies and address the unique needs of each audience. That’s because they may have several products or services aimed at different audiences requiring different types of buyer personas. For example, a business-to-consumer (B2C) company like Ford is likely to have very different personas when it comes to buyers of their rugged F-150 truck, their sporty Mustang Bullitt, and their eco-friendly Escape Hybrid.
Similarly, a business-to-business (B2B) company may have different personas because they target both members of the C-suite and administrative assistants. Both of these potential buyers may be able to use the same product or service, but have very different reasons for wanting it, necessitating a change in how it is marketed to each.
When creating personas, the main thing to remember is to be empathetic. That is, you need to try to get in touch with the needs, feelings, challenges, pain points, goals, and motivations of your audience. Through empathy, strong buyer personas emerge. It’s also important to regularly conduct a sense check to ensure your buyer personas remain accurate and relevant as market conditions and customer behaviors evolve.
Buyer Persona Examples
Let’s see how a buyer persona may look for a hypothetical company that sells exercise equipment. The company has developed a buyer persona for someone they call “Millennial Mark,” using demographic and psychographic data. Millennial Mark and consumers like him are their main target audience. Companies should identify their key buyer personas to focus their marketing strategies and ensure their efforts are directed toward the most impactful segments.
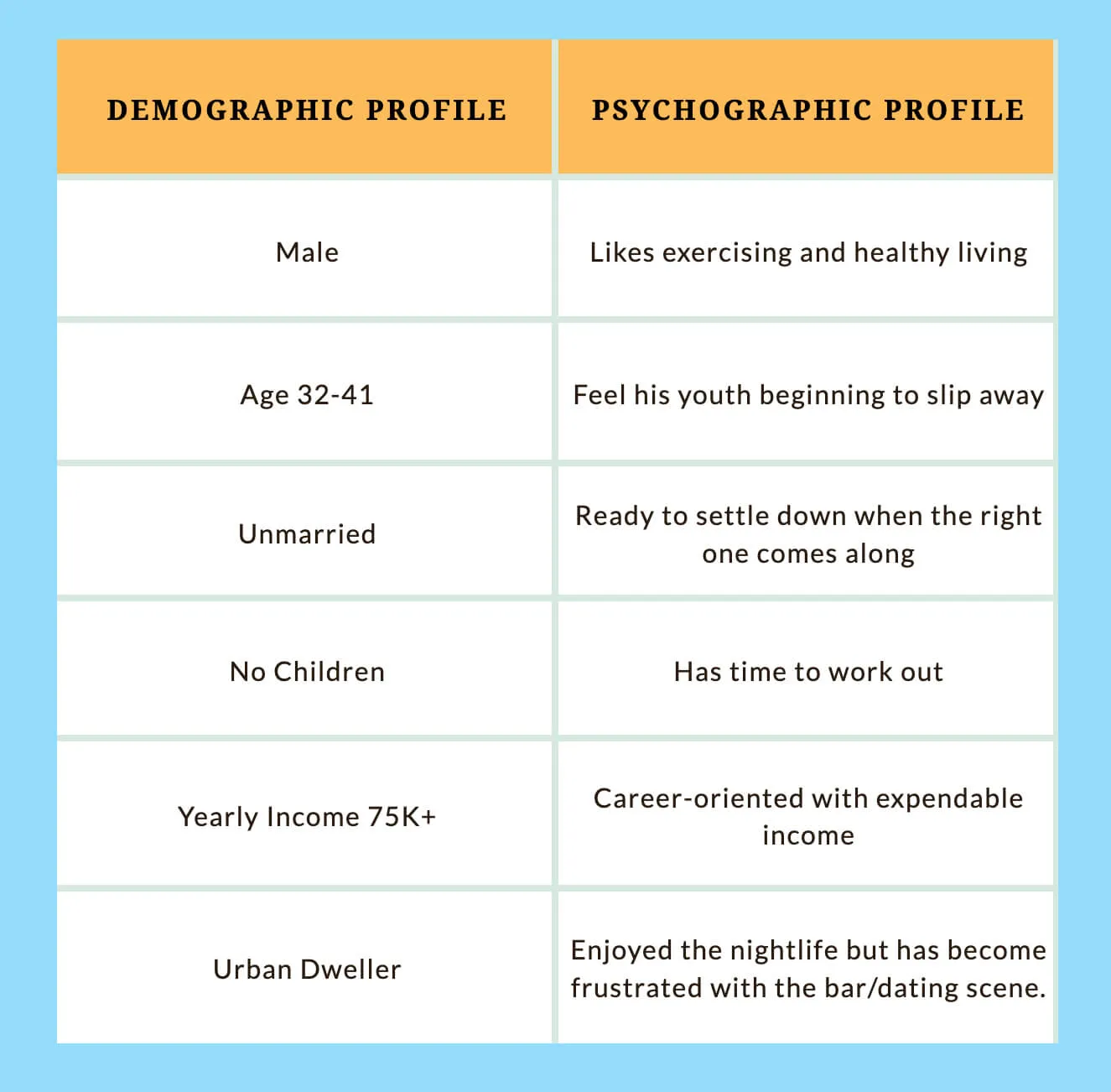
Now, this company could have other personas. They may also be marketing to “Boomer Barbara,” who is an older female looking to maintain her health in her golden years. They may also be marketing their equipment to gyms and fitness centers, meaning not only do they have B2C personas, but B2B personas. In this case, they may have a persona named “Gym Owner John,” and his needs are focused not on his own health or fitness goals, but on bringing in new customers by offering the latest and greatest equipment. When developing personas, it’s important to consider both prospective customers and existing customers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the market and uncover new growth opportunities. Again, each persona will likely be marketed to differently.
Using Surveys to Inform Buyer Personas
As mentioned previously, educated guesses are allowed when developing personas; most companies have some idea of who is buying their products and services. However, guessing can only get you so far. To create true buyer personas, it’s helpful to engage with past and current buyers to learn more about them. It’s also important to include target prospects in your research, as understanding potential customers can reveal new opportunities and help align your marketing efforts.
Some companies hold interviews and focus groups as a type of survey method, but this can be time-consuming and expensive, especially if you have a large number of prospects and customers across a wide geographical span. An easier way to quickly obtain feedback from a wide variety of people is through online surveys. To ensure your buyer personas are comprehensive and accurate, gather data from multiple sources such as social media, customer feedback, and market trends.
SurveyLegend is a free online survey tool that you can start using today. Plus, SurveyLegend’s real-time analytics can help you to easily uncover patterns and trends in order to develop quality personas quickly. These analytics also enable companies to adapt quickly to changes in consumer behavior and external factors like market shifts or technological advancements.
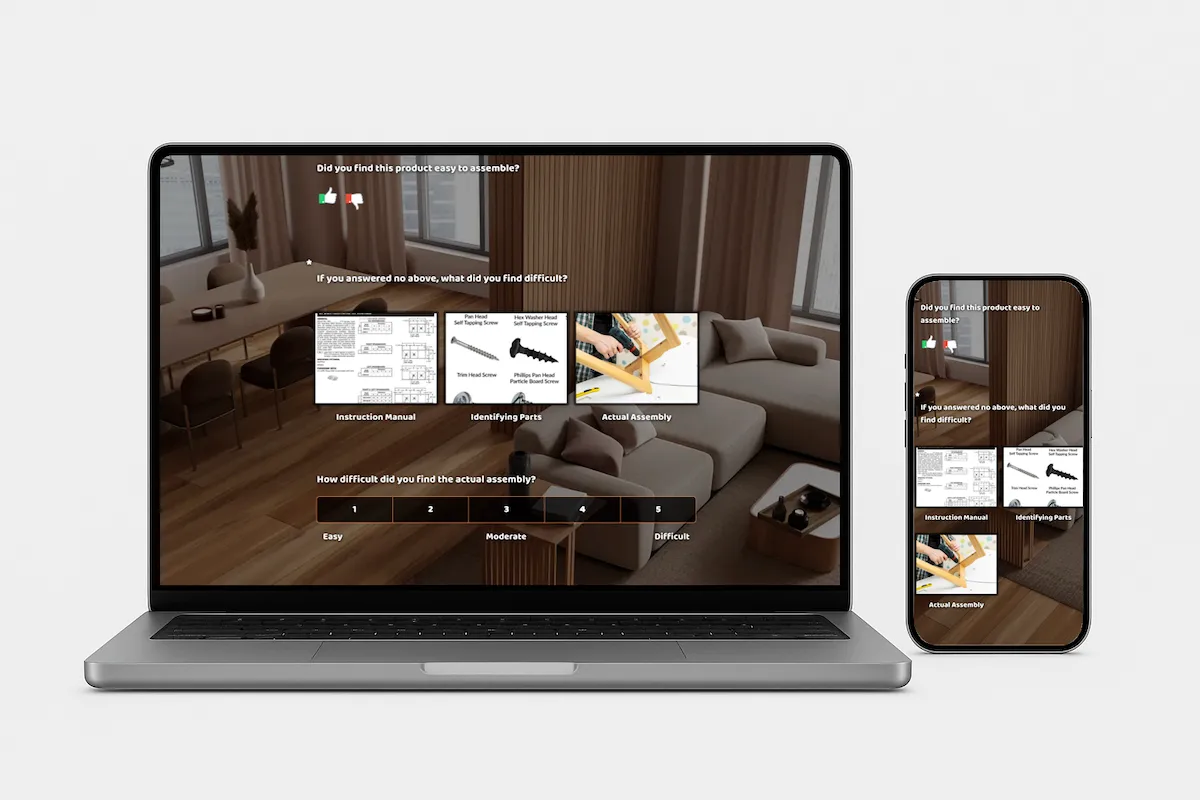
Below is a SurveyLegend survey with buyer persona questions based on our previous example regarding a company selling exercise equipment. You can see from these questions (and SurveyLegend allows you to use many types of survey questions, many included here) how the company was able to put together the buyer persona for Millennial Mark based on answers received from this online survey. You’ll also notice one open-ended question at the end of the survey – this is important for collecting any other information you may not thought to ask of respondents.
This survey is live – try it now for yourself to see SurveyLegend in action!
Securing buy-in from stakeholders is essential to ensure the successful implementation and adoption of your buyer persona strategies.
Analyzing Survey Data
Once you’ve collected survey responses, the next step in creating detailed buyer personas is to analyze the data for actionable insights. Start by segmenting your responses to identify trends and correlations within different buyer groups—such as by company size, industry, or age group. This segmentation helps you pinpoint common pain points, motivations, and goals among your target audience.
To strengthen your findings, supplement survey data with information from your CRM and sales figures. This multi-source approach ensures your buyer personas are grounded in real data, not just assumptions. Tools like Qualtrics iQ can help you dig deeper, using predictive analytics to uncover hidden patterns and additional insight into your audience’s behavior.
For example, a company like Duolingo might analyze survey data to discover that younger users are motivated by gamification and social sharing, while older users value structured lessons and progress tracking. These insights allow marketing teams to craft targeted marketing messages and campaigns that resonate with each segment, improving the overall customer experience and driving more sales. By thoroughly analyzing your survey data, you can create buyer personas that guide your marketing and sales strategies with confidence.
Age Group and Buyer Personas
Age group is a crucial factor when creating detailed buyer personas, as it directly influences your target audience’s preferences, behaviors, and pain points. Different age groups interact with brands in unique ways—while millennials and Gen Z may prefer discovering new services through social media and engaging with interactive content, older generations might respond better to email campaigns or traditional advertising.
Understanding the age group of your target customer allows you to tailor your marketing efforts and create relevant content that speaks to their specific needs. For instance, if your buyer persona research reveals that your ideal customer is in the 25–34 age range, focusing on visually engaging social media campaigns and mobile-friendly surveys can boost engagement and customer loyalty. Conversely, if your audience skews older, providing clear, informative content through trusted channels can help build trust and drive conversions.
By factoring age group into your buyer persona profile, you ensure your marketing messages and campaigns are aligned with your audience’s expectations, leading to more effective marketing strategies and a stronger connection with your customer base.
Top Five Benefits of Buyer Personas
More than 90% of businesses that exceed their revenue goals use buyer personas to segment their database and target customers more effectively. This is because buyer personas offer many benefits, including:
Create highly focused marketing
Once you understand your buyers and all their intricacies, you can move from “one-size-fits-all” marketing, which often results in vague or ambiguous campaigns, to targeted, more personalized marketing that gets results. This targeted approach can lead to improved conversion rates and higher click-through rates, directly impacting your marketing performance.
Create a more customer-centric culture
Often, companies market to whom they think their target audience is without knowing who they really are. This can lead to a bad customer experience. With deep knowledge of who your customer is, cultivated through buyer persona surveys, you can eliminate the mystery (and the guessing) and go to market with confidence.
Get more qualified leads
Understanding your audience means more targeted messaging. And more targeted messaging means more qualified leads. When your potential buyers realize that, “hey, this company really gets me,” they’ll be more open to being marketed and sold to.
Improve the customer experience
When you know your customer, you can anticipate their needs and objections, leading to a better customer experience (CX). You can also tailor content to them (e.g., blogs, offers, and so on) so that it will be more appealing. Choosing the right content formats is crucial, as different buyer personas engage more with certain formats, which can increase interaction and overall engagement.
Tailor your advertising spend
Once you understand your customer, you can adjust your marketing mix to reach them where they’re likely to be. Do they watch a lot of TV? Broadcast may be the way to go. Are they online 24/7? Funnel that money into online ads. Do they spend two hours a day commuting? Reach them through the radio.
Conclusion
Winging a sales or marketing strategy is no way to rise above the competition or grow a loyal customer following. To be sure you’re marketing to the right people – and using the right marketing messages – having well-crafted buyer personas is a must.
To create them, surveys are your friend. And, when it’s time to survey, SurveyLegend is your best friend. You can count on our free survey maker for beautiful and secure online surveys, along with quality data and analytics. Get started today and begin creating your buyer personas in no time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the buyer persona definition?
A leader in buyer personas, Hubspot defines a buyer persona as “a semi-fictional representation of your ideal buyer based on data, interviews, and some educated guesses. Essentially, it’s a definition of your ideal buyer presented in such a way that it sounds like it’s talking about a specific person.”
What are the elements of a buyer persona?
Buyer personas should include demographic information (e.g., age, gender, income, location, profession, and so on) and psychographic information (hobbies and interests, values and goals, aspirations and motivations, challenges and pain points, etc). When targeting B2B individuals, it’s also important to consider specifics about their company (industry, number of employees, years in business, market share, business challenges, and so on).
What are some considerations for a buyer persona survey?
When crafting a buyer persona survey, include questions that cover both factual items, such as which brands they like, and “drivers,” which are their motivations, values, and goals.